Grade 8- Water and the Earth's atmosphere
Welcome grade 8T and 8N
We have completed the Respiratory system and now we are look at WATER AND THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE
Pages 164-172 in your text book.
Pages 164-172 in your text book.
Please recap the process involved in the Water Cycle shown below.
The water that settles under ground is called Groundwater. The largest use for groundwater is to irrigate crops.
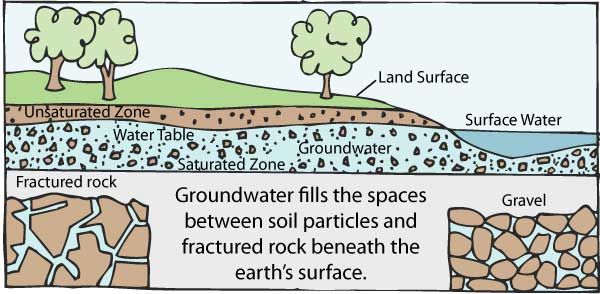
The area where water fills the aquifer is called the saturated zone (or saturation zone). The top of this zone is called the water table. The water table may be located only a foot below the ground’s surface or it can sit hundreds of feet down.

Aquifers are typically made up of gravel, sand, sandstone, or fractured rock, like limestone. Water can move through these materials because they have large connected spaces that make them permeable. The speed at which groundwater flows depends on the size of the spaces in the soil or rock and how well the spaces are connected.
Groundwater can be found almost everywhere. The water table may be deep or shallow; and may rise or fall depending on many factors. Heavy rains or melting snow may cause the water table to rise, or heavy pumping of groundwater supplies may cause the water table to fall.

Groundwater supplies are replenished, or recharged, by rain and snow melt that seeps down into the cracks and crevices beneath the land's surface. In some areas of the world, people face serious water shortages because groundwater is used faster than it is naturally replenished. In other areas groundwater is polluted by human activities.
Water in aquifers is brought to the surface naturally through a spring or can be discharged into lakes and streams. Groundwater can also be extracted through a well drilled into the aquifer. A well is a pipe in the ground that fills with groundwater. This water can be brought to the surface by a pump. Shallow wells may go dry if the water table falls below the bottom of the well. Some wells, called artesian wells, do not need a pump because of natural pressures that force the water up and out of the well.
In areas where material above the aquifer is permeable, pollutants can readily sink into groundwater supplies. Groundwater can be polluted by landfills, septic tanks, leaky underground gas tanks, and from overuse of fertilizers and pesticides. If groundwater becomes polluted, it will no longer be safe to drink.
Surface Water
Surface water is water that collects on the ground or in a stream, river, lake, reservoir, or ocean. Surface water is constantly replenished through precipitation, and lost through evaporation and seepage into ground water supplies. Most community water system users received their water from a surface water source, such as a lake.
Here are two videos that you should view to further explain ground and surface water.
Reference
https://www.groundwater.org/get-informed/basics/whatis.html
https://www.cdc.gov/healthywater/drinking/public/water_sources.html




Comments
Post a Comment